New Mechanochemical Pathway to Sustainable Metals
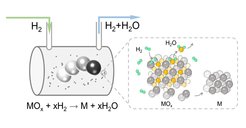
The reduction of metal oxides is a crucial step in metallurgy, catalyst synthesis, nanoparticle synthesis, powder metallurgy, and additive manufacturing. Especially in the metallurgy sector, high temperature and carbon-containing reducing agents such as C and CO are often used for the reduction of metal oxides, resulting in high-energy consumption and intensive CO2 emissions. We find that metal oxides can be efficiently reduced at low or even room temperature using mechanical energy input via a ball milling process and a hydrogen stream as a reducing agent. Efficient mechanochemical reduction benefits from the creation of numerous oxygen vacancies, an increased surface area, a continuously renewed particle surface, and a constant removal of moisture. This offers an emission-free and energy-efficient pathway to reduce metal.
